[Melvin B] Writing Practice Test 1408097
Task 1
You should spend about 20 minutes on this task.
The pie charts below show the percentage of time working adults spent on different activities in a particular country in 1958 and 2008. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant
You should write at least 150 words.
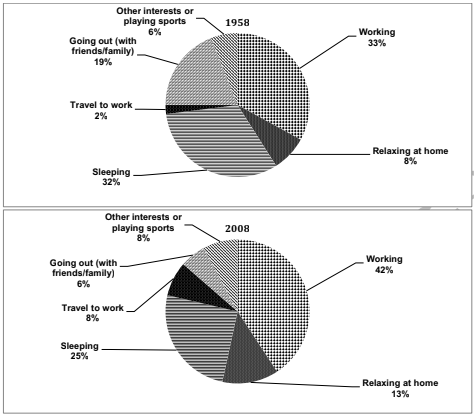
This summary serves as a concise report detailing the trends within a specific nation from 1958 to 2008. Commencing in 1958, the provided diagram illustrates that 6% of individuals devoted their entire day to various sports activities. However, by 2008, this percentage had risen from 6% to 8%. Additionally, the data indicates that in 1958, 19% of people spent their daily time engaging with friends and family, yet in 2008, this figure plummeted to a remarkable 6%.
Regarding travel, the percentage indicated in 1958 with two decimal places escalated to 8% in 2008. Conversely, sleeping time, which constituted 32% in 1958, decreased to 25% overall. Meanwhile, the percentage of relaxation time rose from 13% in 1958 to 13% in 2008. Considering the working population category, which stood at 33% in 1958, it increased to 42% overall, accounting for the entire 100% when all factors are taken into account.
Task 2
You should spend about 40 minutes on this task.
Nowadays, not enough students choose science subjects in university in many countries. What are the reasons for this problem? What are the effects on society?
You should write at least 250 words.
The declining enrollment of students in science subjects at the university level across numerous countries is a multifaceted issue with roots in various factors. One significant contributing factor is the perceived difficulty associated with science disciplines. Students may shy away from pursuing these subjects due to apprehensions about the complexity and demanding nature of the curriculum. This perceived difficulty, often exacerbated by inadequate foundational education or instructional methodologies, deters potential science enthusiasts.
Furthermore, there exists a prevailing issue of limited exposure to real-world applications of science during earlier education stages. The lack of hands-on experiences and practical demonstrations can lead to a diminished interest and understanding of the tangible impacts and relevance of scientific knowledge. This gap in connecting theoretical learning with practical implications may contribute to a disinterest in pursuing science-related fields at the university level.
Societal factors also play a pivotal role in steering students away from science subjects. Prevailing preferences and societal pressures often influence students to opt for disciplines perceived as more lucrative or prestigious, such as business or technology-related fields. This inclination is driven by societal norms and expectations, creating a shift in focus away from the intrinsic value of scientific inquiry.
In addition, the shortage of qualified science educators and inadequate infrastructure in certain educational institutions may pose challenges to fostering a conducive learning environment for science subjects. The absence of well-equipped laboratories, research facilities, and expert guidance can hinder students' engagement and practical exploration in scientific disciplines.
The consequences of the declining interest in science subjects reverberate across societal and economic dimensions. A shortage of skilled professionals in crucial scientific fields, including research, healthcare, and technology, can impede advancements and innovations. This, in turn, may impact a nation's competitiveness on the global stage. Moreover, a society with a reduced emphasis on science education may face challenges in addressing complex issues, such as environmental concerns and health crises, which require a robust foundation in scientific knowledge.
Addressing this issue necessitates comprehensive educational reforms, including curriculum enhancements that emphasize practical applications, hands-on experiences, and interdisciplinary approaches to ignite students' interest in science. Additionally, promoting the societal value of scientific pursuits through awareness campaigns and advocacy can play a pivotal role in shifting perceptions and encouraging students to embrace the opportunities presented by science-related disciplines.
Community’s feedback
Sorry! We couldn't find any contents.
Score Given by Community
Give a bandscoreLeaderboard:
| # | User | Score | Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subid Basaula |  | 7.0 | 59:58 | |
| Yuki Arai |  | 6.5 | 58:09 | |
| Gayane Aramyan |  | 6.0 | 49:19 |



